The malaria parasite life cycle involves two hosts. A data set comprising 13 An.
 Mosquito Borne Diseases Debugged
Mosquito Borne Diseases Debugged
For each mosquito population six to nine plastic trays ie.

Water content malaria mosquito population. Are exposed to large seasonal and daily fluctuations in relative humidity and temperature which makes coping with drought a crucial aspect of their ecology. Melas or 17 An. Mosquito population growth rates.
Consequently it is important to understand the biology of malaria vector mosquitoes in the study. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. Soumousso 1104 N 403 W located in the south of Bobo-Dioulasso in contrast with VK3 it is a drier setting where the dominant species are An.
Mosquitoes emerge from a water source uninfected and unfed S uSusceptible unfed mosquitoes feed at rate A u and they are then considered fed and susceptible S f unless the blood-meal infects the mosquito with malaria with probability cX in which case they become latent. To better understand natural variation in desiccation resistance in this species the effects of variation in larval food availability and access to water as an adult on. Population modification strategies employing gene-drive systems to spread anti-parasite effector molecules through populations of Anopheles mosquitoes are gaining momentum in the fight against.
Of note in P. Discussion81 In a water-limited environment such as the Sahel land surface hydrology controls malaria mosquito population dynamics. Inter-village differences in local hydrology can lead to unequal extents of suitable breeding.
In malaria eco-epidemiology landscape components atmosphere water bodies land use interact with the epidemiological system interacting populations of vector human and parasite. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever tiredness vomiting and headaches. Here we use a stochastic simulation model to explore the potential of using a driving-Y chromosome to suppress vector populations in a 106 km2 area of West Africa.
Our aim was to ascertain the effect of beer consumption on human attractiveness to malaria mosquitoes in semi field. The observed temperature differences lead to large differences in estimated development times with higher mean water temperatures shortening larval duration by 40-44 days equivalent to 25-28 in Kisian and by 97-112 days equivalent to 39-45 in Lyanaginga and Fort Ternan compared with estimates based on the mean air temperatures Figure 3. In severe cases it can cause yellow skin seizures coma or death.
After hatching first instar larvae were readily transferred into new plastic trays filled with 1 l of deionised water at an optimal growing density of about 200 larvae per tray. The sudden appearance of widespread but temporary water pools gives rise to a rapid increase in mosquito populations clustered around human habitation resulting in the highly focal malaria transmission that is a characteristic of Sahel villages 12. The persistence of malaria in large parts of sub-Saharan Africa has motivated the development of novel tools to complement existing control programmes including gene-drive technologies to modify mosquito vector populations.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. During a blood meal a malaria-infected female Anopheles mosquito inoculates sporozoites into the human host Sporozoites infect liver cells and mature into schizonts which rupture and release merozoites. Malaria is a mosquito-transmitted parasitic disease which still kills more than 400000 people and infects more than 200 million people worldwide annually with 90 of the cases in Africa Malaria cases and mortality have shown dramatic reductions between 2000 and 2015 primarily due to vector control but progress may be plateauing.
Man-made areas of stagnant water eg paddy fields. Cumulative mosquitoes observed and model outputmodel results. Malaria parasites are entirely dependent on Anopheles mosquitoes for transmission.
For this reason vector population dynamics is a crucial determinant of malaria risk. Settlements provide large populations for. Malaria transmission dynamics within a patch between mosquito and human population.
Gambiae and a mixture of mostly Anopheles funestus Anopheles arabiensis Anopheles coluzzii In this area the mosquito density is lower compared to that of Vallée du Kou and the dynamics of the mosquito population follow the two main. Natural populations of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae ss. Inter-village differences in local hydrology can lead to unequal extents of suitable breeding habitat following rain and conse-.
As previously mentioned neither superinfection nor immune response as a function of inoculation rates are represented in the model. Ovale a dormant stage hypnozoites can persist in the liver if untreated and cause relapses by invading. If not properly treated people may have recurrences of the.
Alcohol consumption is rising in developing countries and as efforts to manage malaria are expanded understanding the links between malaria and alcohol consumption becomes crucial. In the background of the eco-epidemiological approach a mosquito population model is here proposed to evaluate the sensitivity of An. Background Malaria and alcohol consumption both represent major public health problems.
About 12001800 larvae were used for each experimental condition RS ODS. Malaria continues to be one of the most devastating diseases in the world killing more humans than any other infectious disease. Mosquito population in blue.
Malaria is spread as the female anopheles mosquito bites a person and the parasite is passed into. Temporary water pools gives rise to a rapid increase in mosquito populations clustered around human habita-tion resulting in the highly focal malaria transmission that is a characteristic of Sahel villages 12. Gambiae microsatellite markers was obtained for a total 1519 mosquitoes from the study populations Figure 1 from Equatorial GuineaThis data represents 2 to 4 time points for each of the seven populations included in this study Table 1After discarding markers showing evidence for the presence of null alleles.
Between 2000 and 2015 insecticide-based control interventions targeting mosquito vectors averted an estimated 537 million malaria cases 1Nevertheless malaria still kills hundreds of thousands of people each year 445000 in 2016 mainly in sub-Saharan Africa 2Additionally there is concern that progress may have stalled after more than a decade of success in global malaria control 2.
 Awesome World Malaria Day Infographic From Macepa Malaria Control And Evaluation Partnership In Africa At Path Malaria Infographic Malaria Investing
Awesome World Malaria Day Infographic From Macepa Malaria Control And Evaluation Partnership In Africa At Path Malaria Infographic Malaria Investing
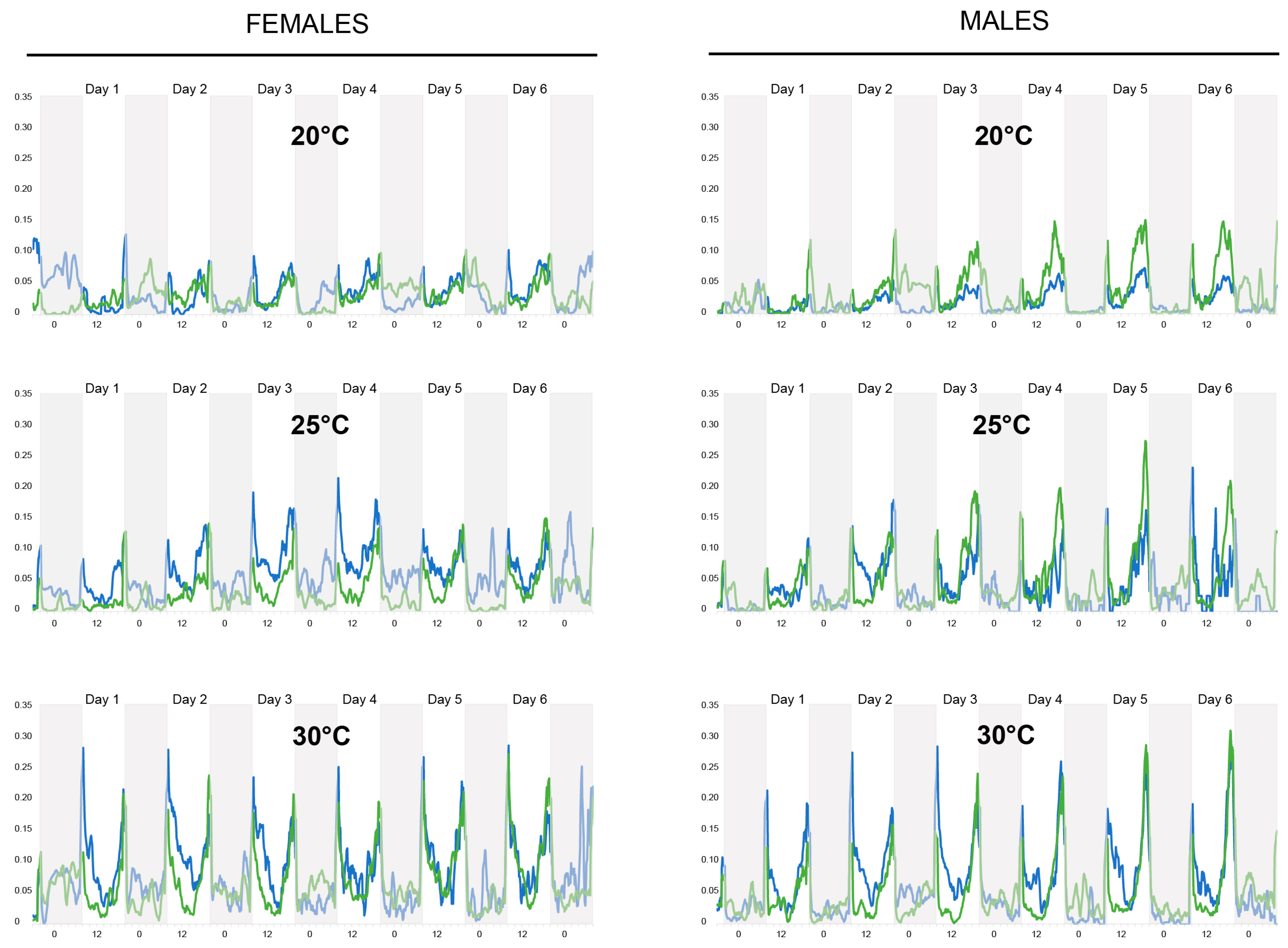 Insects Free Full Text Temperature And Sugar Feeding Effects On The Activity Of A Laboratory Strain Of Aedes Aegypti Html
Insects Free Full Text Temperature And Sugar Feeding Effects On The Activity Of A Laboratory Strain Of Aedes Aegypti Html
 The Above Map Shows Areas Of Water Stress In Sub Saharan Africa 37 Of The Worlds Population That Lacks Access To Access To Clean Water Water Life Safe Water
The Above Map Shows Areas Of Water Stress In Sub Saharan Africa 37 Of The Worlds Population That Lacks Access To Access To Clean Water Water Life Safe Water
 California Braces For More Rain How Bad Can It Get Published 2017 Humming Bird Feeders California Drought Bees And Wasps
California Braces For More Rain How Bad Can It Get Published 2017 Humming Bird Feeders California Drought Bees And Wasps
Https Www Contracostamosquito Com Pdf Ccm Bpm Pdf
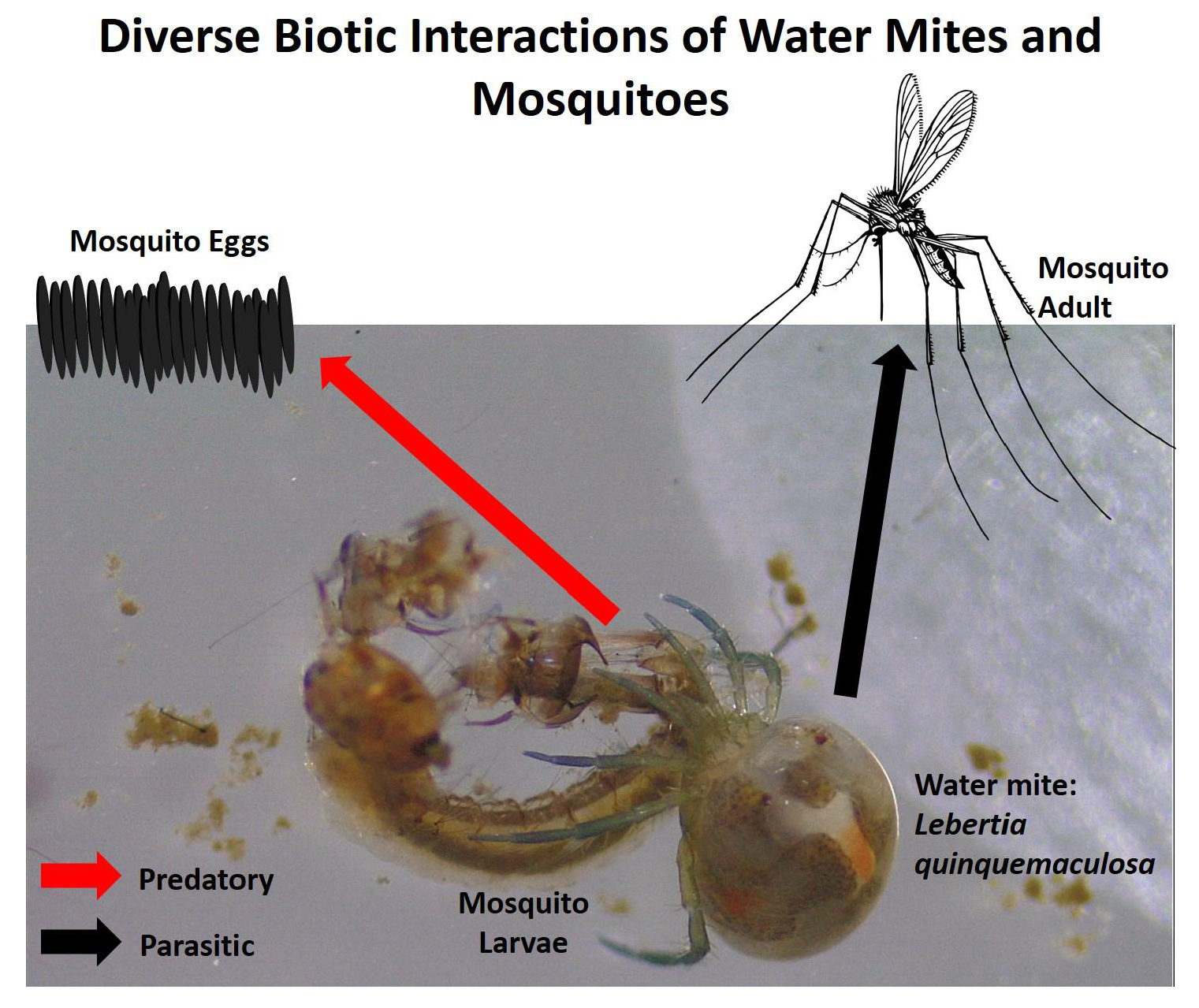 Diversity Free Full Text The Biodiversity Of Water Mites That Prey On And Parasitize Mosquitoes Html
Diversity Free Full Text The Biodiversity Of Water Mites That Prey On And Parasitize Mosquitoes Html
 Manage Standing Water To Reduce Mosquito Disease Threat Cropwatch University Of Nebraska Lincoln
Manage Standing Water To Reduce Mosquito Disease Threat Cropwatch University Of Nebraska Lincoln
 Oxford Medicine As The Consequences Of Climate Change Become More Apparent There Has Been Increasing Awareness About How To Stay Healthy Travel Kits Health
Oxford Medicine As The Consequences Of Climate Change Become More Apparent There Has Been Increasing Awareness About How To Stay Healthy Travel Kits Health
 Mosquitoes And The Triple E Threat What You Need To Know
Mosquitoes And The Triple E Threat What You Need To Know
 Information On A Mosquito S Life Cycle Terminix Blog Mosquito Mosquito Life Cycle Life Cycles
Information On A Mosquito S Life Cycle Terminix Blog Mosquito Mosquito Life Cycle Life Cycles